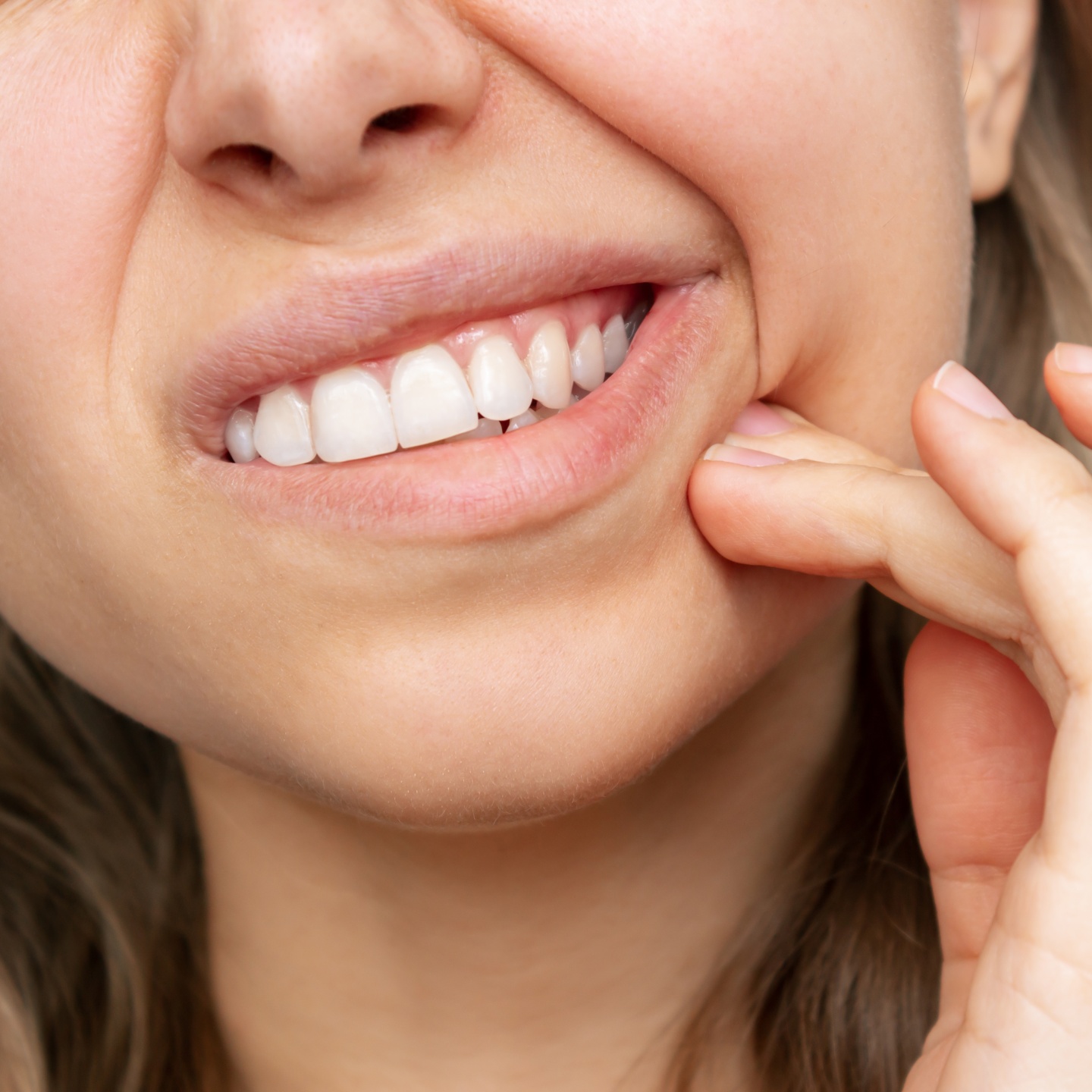
The procedure can range from simple extractions to more complex surgical removals, depending on the tooth’s position and eruption status.
Also known as third molars, they are the last set of molars to emerge, typically appearing between the ages of 17 and 25. They are not always problematic, but often they don’t have enough space to fully erupt or grow properly, leading to various issues.
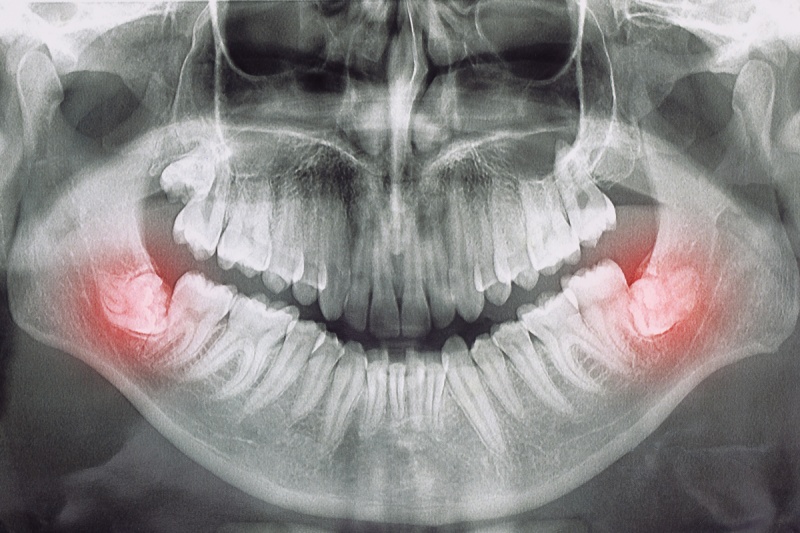
Wisdom teeth can become impacted, meaning they are trapped under the gum or bone and cannot fully emerge. This can cause pain, infection, and damage to neighbouring teeth.
Impacted or misaligned wisdom teeth can cause persistent pain, jaw stiffness, and headaches.
Impacted wisdom teeth create a space where bacteria can accumulate, leading to infections (pericoronitis).
Wisdom teeth can push other teeth out of alignment, affecting the bite and potentially requiring orthodontic treatment.
In rare cases, cysts or tumours can develop around impacted wisdom teeth.
A dentist or oral surgeon will take X-rays /CBCT (3d scan) to assess the position and development of the wisdom teeth. They will determine the best course of action, whether it’s a simple extraction or a surgical removal.
Local anaesthesia is used to numb the area. Sedation or general anaesthesia may be used for more complex cases or patient anxiety.
Stitches may be used to close the gum, and dissolvable stitches are often used.
